“`html
The Importance of Sustainability Science
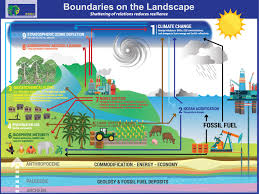
Sustainability science is a multidisciplinary field that aims to address the complex challenges facing our planet and its inhabitants. It integrates knowledge from various disciplines such as environmental science, social science, economics, and technology to develop solutions that promote long-term ecological balance, social equity, and economic prosperity.
One of the key aspects of sustainability science is its focus on understanding the interconnectedness of environmental, social, and economic systems. By studying these interrelationships, researchers in this field can identify sustainable practices that not only protect the environment but also enhance human well-being and support economic development.
Through sustainability science, experts work towards finding innovative ways to conserve natural resources, reduce pollution, mitigate climate change impacts, and promote sustainable development. This holistic approach considers the needs of present and future generations, aiming to create a more resilient and equitable society.
Furthermore, sustainability science emphasizes collaboration and engagement with diverse stakeholders including policymakers, businesses, communities, and individuals. By fostering partnerships and knowledge-sharing among different sectors, sustainable solutions can be implemented more effectively on a local, regional, and global scale.
In conclusion, sustainability science plays a crucial role in shaping a more sustainable future for our planet. By integrating scientific research with practical applications and societal values, this field offers hope for addressing pressing environmental challenges while fostering a more equitable and prosperous world for all.
“`
8 Key Benefits of Sustainability Science: Advancing Ecological Balance and Human Well-Being
- Promotes long-term ecological balance
- Addresses complex environmental challenges
- Integrates knowledge from various disciplines
- Supports sustainable development goals
- Fosters innovation in conservation practices
- Enhances human well-being and quality of life
- Encourages collaboration among diverse stakeholders
- Contributes to building a resilient and equitable society
Challenges in Sustainability Science: Navigating Complexity, Resource Demands, and Resistance to Change
Promotes long-term ecological balance
Sustainability science’s promotion of long-term ecological balance is a crucial benefit that ensures the health and vitality of our planet for future generations. By emphasizing practices that support the well-being of ecosystems and biodiversity over time, sustainability science aims to preserve natural resources and maintain the delicate balance of our environment. This proactive approach not only safeguards the Earth’s ecosystems but also contributes to a more sustainable and resilient planet that can continue to provide essential resources for all living organisms.
Addresses complex environmental challenges
Sustainability science excels in addressing complex environmental challenges by employing a holistic and interdisciplinary approach. By integrating knowledge from various fields such as ecology, climate science, and social sciences, sustainability science can effectively analyze the intricate connections between human activities and the environment. This comprehensive understanding enables researchers to develop innovative solutions that not only mitigate environmental degradation but also promote sustainable practices that benefit both ecosystems and societies. Through its focus on complexity and interconnectedness, sustainability science offers valuable insights and strategies for tackling the most pressing environmental issues of our time.
Integrates knowledge from various disciplines
Sustainability science stands out for its ability to integrate knowledge from various disciplines, allowing for a comprehensive and holistic approach to addressing environmental and social challenges. By drawing upon insights from fields such as environmental science, social science, economics, and technology, sustainability science can offer innovative solutions that consider the interconnected nature of our world. This interdisciplinary approach not only enriches the depth of analysis but also enables the development of more effective strategies that take into account the complexities of sustainability issues. Ultimately, by leveraging diverse expertise and perspectives, sustainability science can lead to more informed decision-making and impactful actions towards creating a more sustainable future for all.
Supports sustainable development goals
“`html
Sustainability science plays a vital role in supporting sustainable development goals by providing a framework for addressing global challenges while promoting economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental protection. Through its interdisciplinary approach, sustainability science helps identify innovative solutions that contribute to achieving the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). By integrating knowledge from various fields and engaging diverse stakeholders, sustainability science facilitates the implementation of strategies that promote sustainable development in a holistic and inclusive manner, ultimately working towards a more equitable and resilient future for all.
“`
Fosters innovation in conservation practices
Sustainability science fosters innovation in conservation practices by encouraging the development of creative and effective solutions to protect natural resources and biodiversity. Through interdisciplinary collaboration and research, sustainability scientists explore new technologies, strategies, and approaches that can enhance conservation efforts. By promoting innovation in conservation practices, sustainability science helps address environmental challenges more efficiently and sustainably, ensuring the long-term health of ecosystems and the well-being of both present and future generations.
Enhances human well-being and quality of life
Sustainability science, by promoting practices that enhance human well-being and quality of life, plays a vital role in creating a more prosperous and equitable society. By focusing on sustainable development, conservation of natural resources, and reducing environmental degradation, sustainability science not only safeguards the health and livelihoods of current generations but also ensures a better future for generations to come. Through its emphasis on improving living standards, fostering social equity, and addressing health disparities, sustainability science contributes to creating communities where individuals can thrive in harmony with their environment.
Encourages collaboration among diverse stakeholders
Sustainability science excels in encouraging collaboration among diverse stakeholders, fostering a collective approach to addressing environmental and social challenges. By bringing together individuals from various backgrounds, including policymakers, businesses, communities, and experts from different fields, sustainability science promotes the sharing of knowledge, resources, and innovative ideas. This collaborative effort not only leads to more comprehensive and effective solutions but also ensures that the needs and perspectives of all stakeholders are taken into account. Ultimately, by working together towards common sustainability goals, diverse stakeholders can create positive impacts that benefit both the environment and society as a whole.
Contributes to building a resilient and equitable society
Sustainability science contributes significantly to building a resilient and equitable society by promoting practices that enhance social equity and environmental resilience. By integrating knowledge from various disciplines and fostering collaboration among stakeholders, sustainability science helps identify solutions that not only protect the environment but also address social inequalities. Through sustainable practices, communities can become more resilient to environmental challenges and economic disruptions, ensuring a more equitable distribution of resources and opportunities for all members of society. This proactive approach not only strengthens the fabric of society but also creates a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Complexity
The con of complexity in sustainability science poses a significant challenge in navigating and implementing sustainable practices. With its wide range of disciplines and factors, sustainability science requires a deep understanding of various interconnected systems, which can be overwhelming for researchers and practitioners. The complexity of the field can lead to difficulties in identifying effective solutions, coordinating efforts across different sectors, and communicating findings to diverse stakeholders. Despite its challenges, addressing the complexity of sustainability science is essential to ensure comprehensive and impactful responses to pressing environmental and social issues.
Resource Intensive
One notable con of sustainability science is its resource-intensive nature. The process of conducting research and implementing sustainable practices often demands substantial resources in terms of time, funding, and expertise. Researchers and practitioners in this field may face challenges in securing adequate funding for their projects, which can hinder the scale and impact of their efforts. Additionally, the complexity of sustainability issues requires a diverse range of expertise, leading to the need for multidisciplinary collaborations that can be time-consuming to establish and maintain. Despite these challenges, finding ways to streamline resource allocation and increase efficiency in sustainability science endeavors is essential to overcome this con and maximize the positive outcomes of sustainable practices.
Resistance to Change
“`html
Resistance to change is a significant con of sustainability science as it involves challenging established norms and practices. Embracing sustainability science often necessitates a shift away from traditional methods, which can be met with resistance from industries or individuals comfortable with the status quo. This resistance may stem from concerns about potential disruptions to existing operations, fear of unknown outcomes, or reluctance to invest in new technologies or practices. Overcoming this resistance requires effective communication, education, and collaboration to demonstrate the benefits of sustainable approaches and facilitate a smooth transition towards a more environmentally friendly and socially responsible future.
“`